What Is a DNS Server?
DNS Meaning – What Does DNS Stand For?
A DNS server is a system that stores and provides information about domain names and how they should be handled on the internet. Its primary job is to answer questions like:
- Where is this website hosted?
- Which server is responsible for handling email for this domain?
- Which DNS provider is managing the domain (such as Google DNS, Cloudflare, or another service)?
Whenever someone visits a website, sends an email, or connects to an online service, a DNS server is consulted to determine where that request should be sent.
Without DNS servers, the internet would not function in a reliable or user-friendly way.
What Does a DNS Server Do?
In simple terms, a DNS server:
- Converts domain names into IP addresses
- Directs website traffic to the correct web server
- Tells email systems where to deliver messages
- Helps apply security and reliability rules for a domain
Every online action that involves a domain name relies on DNS servers working correctly behind the scenes.

Types of DNS Servers Explained
There are several different types of DNS servers, each with a specific role.
Authoritative DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS servers hold the official DNS records for a domain. These records define:
- Website hosting (A and AAAA records)
- Email routing (MX records)
- Verification and security settings (TXT records, SPF, DMARC, DKIM)
If a DNS record needs to be changed, it is updated on the authoritative DNS server.
Recursive DNS Servers
Recursive DNS servers act as lookup agents for users. When you type a website address into your browser, your device asks a recursive DNS server to find the answer.
The recursive server:
- Searches the DNS system on your behalf
- Queries authoritative DNS servers
- Returns the correct IP address to your device
Most users interact with recursive DNS servers provided by their ISP or a public DNS provider.
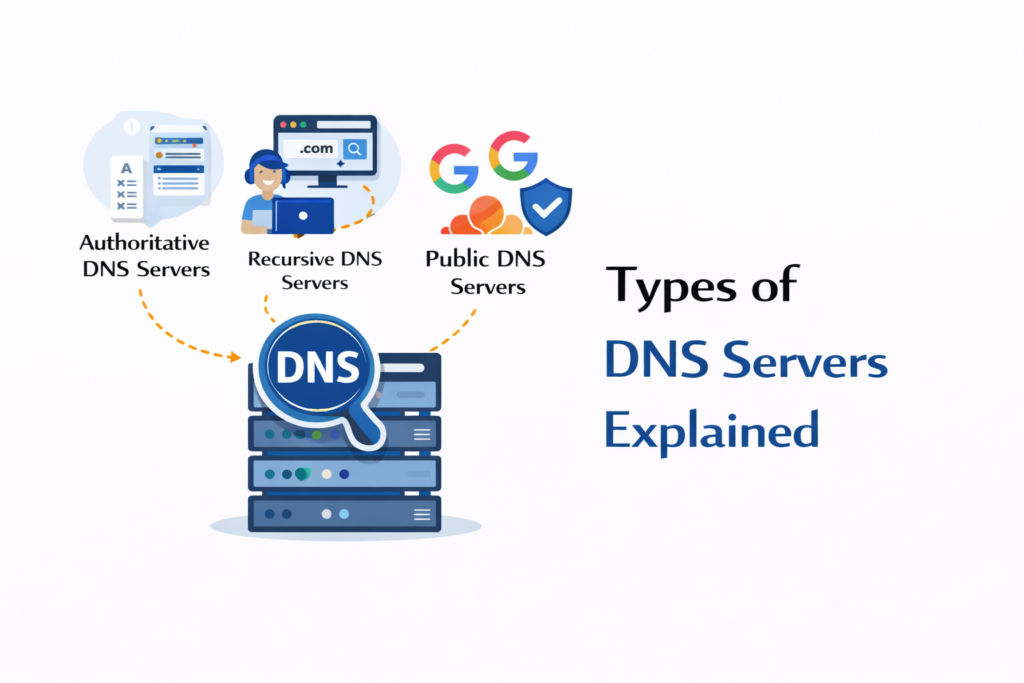
Public DNS Servers
Public DNS servers are widely used recursive DNS services that anyone can choose to use instead of their internet provider’s default DNS.
Popular examples include:
- Google DNS
- Cloudflare DNS
- AdGuard DNS
These services often offer:
- Faster lookup speeds
- Improved privacy
- Enhanced security and filtering

Why DNS Server Configuration Matters
If DNS servers are misconfigured or unavailable, it can lead to:
- Websites not loading
- Emails failing to send or receive
- Security warnings or delivery issues
- Slow or unreliable performance
Even a small DNS error can cause major disruption for a business or online service.

